Arthroscopy : What is Arthroscopy and What Conditions Does it Treat?
749
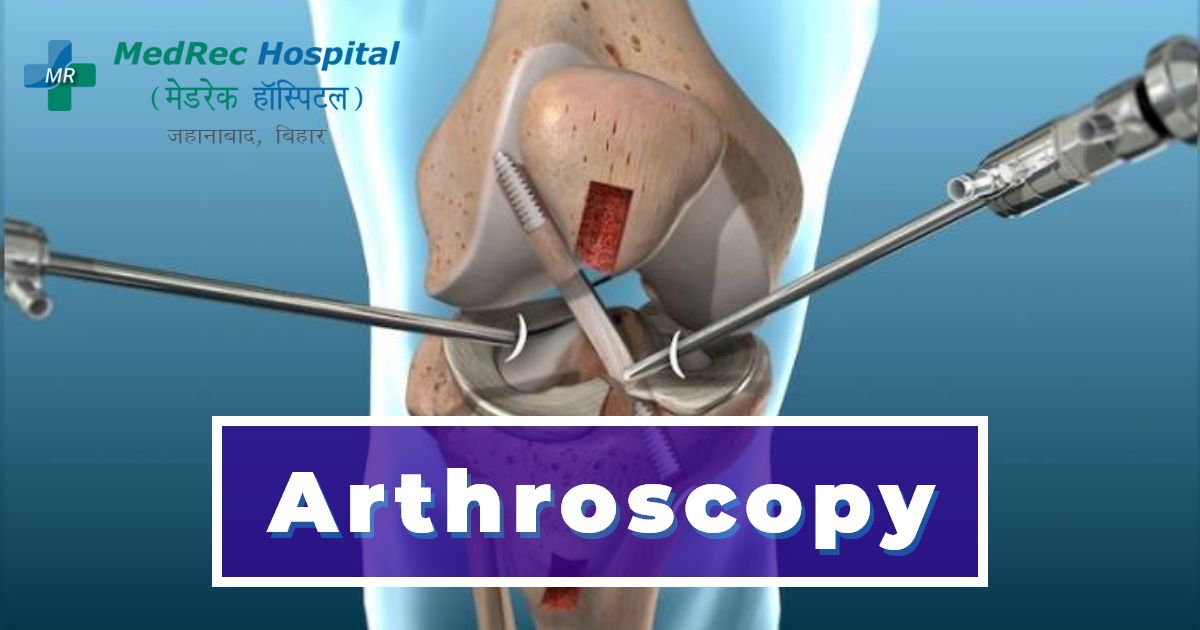
Arthroscopy is a technique used to identify and diagnose joint medical issues. A buttonhole-sized incision is made by the surgeon, and a thin tube connected to a fiber-optic video camera is inserted through it. The video feed from inside your joint is received by a high-definition display.
With arthroscopy, the surgeon may view the interior of your joint without cutting a significant incision. With the use of extra tiny incisions and pencil-thin surgical equipment, surgeons can even fix some forms of joint injury during arthroscopy.
How to check if you require an Arthroscopy?
A variety of joint conditions are diagnosed and treated by doctors using arthroscopy, most frequently those affecting the:
- Knee
- Shoulder
- Elbow
- Ankle
- Hip
- Wrist
When X-rays and other imaging tests are unable to provide all the necessary information for a diagnosis, doctors frequently use arthroscopy as an alternative form of gathering further information.
Risk Factors
Complications are rare with arthroscopy, which makes it a highly safe operation.
Potential risks can be the following:
- Nerve or tissue injury. The structures of the joint may be harmed by how the tools are positioned and moved within it.
- Infection. An infection can happen after any kind of invasive surgery.
- Clots of blood. On rare occasions, operations lasting more than an hour can increase your chances of getting blood clots in your lungs or legs.
Procedure
How to prepare for an arthroscopic procedure:
The type of joint the surgeon is inspecting and fixing will determine the precise preparations needed. The following steps are recommended to best prepare for this surgical procedure:
Steer clear of some drugs. The use of medications or dietary supplements that might increase your risk of bleeding may be discouraged by your doctor.
Avoid solid foods. Your doctor could advise you to refrain from eating solid foods eight hours before your treatment, depending on the sort of anaesthetic you will have.
Organise a lift home. After the treatment, you will not be able to drive yourself home, so arrange for someone to pick you up. Ask someone to check on you that evening if you live alone, or better yet, have them remain with you the rest of the day.
Wear loose-fitting clothes. Wear loose, comfy clothes, such as baggy shorts.
On the day of the procedure
Some steps of arthroscopy are quite common, even though the experience varies based on why you are having the operation and which joint is involved.
- You will take off your outerwear and jewellery, and change into a hospital gown.
- Your hand or forearm will get an intravenous catheter from a nurse, who will also provide a little sedative.
The Procedure:
The anaesthetic that will be used depends on the type of joint surgery.
A local anaesthetic.
Numbing agents are injected under the skin to numb a particular area, like your knee. During an arthroscopy, you will be awake, but the most you will experience is pressure or a sense of movement within the joint.
Regional sedation.
A needle is used to inject the most common type of regional anaesthetic into the area between your lumbar vertebrae. As a result, your lower body goes numb, but you stay conscious.
General sedation
Depending on how long the surgery may take, it could be preferable for you to be asleep. General anaesthesia is given via a vein.
The ideal setting for your treatment will be chosen for you.
The ideal setting for your treatment will be chosen for you. You might do this while lying on your side or back. A tourniquet may be used to reduce blood loss and improve visualisation inside the joint while the affected limb is in a positioning device.
Filling the joint with sterile fluid is another method to enhance the view within your joint. The vicinity of the joint enlarges as a result.
The viewing equipment is accommodated by a single, tiny incision. The surgeon can insert surgical instruments to grab, cut, grind, and apply suction as necessary for joint repair through further tiny incisions at various locations around the joint.
Small enough incisions will just require one or two stitches to close them, or use thin, sterile sticky tape strips.
Post surgery
Arthroscopic surgery is fast. A procedure such as a knee arthroscopy could take less than an hour.After some time spent resting in a different room, you will be taken to a discharge lounge and returned home.
Your aftercare might consist of:
Medications. To treat pain and inflammation, your doctor could recommend medication.
R.I.C.E. To lessen discomfort and swelling, you could find it beneficial to rest, ice, compress, and elevate the joint at home for a few days.
Protection. For comfort and protection, you might need to utilise crutches, slings, or temporary splints.
Exercises. Physical therapy and rehabilitation may be advised by your doctor to help you build up your muscles and enhance the functionality of your joints.
In the event that you experience:
- Fever Pain that is untreated by medicine
- Drainage from your incision
- Swollen area or redness
- Tingling or numbness
Please consult your medical team for further advice.
Treatments
Surgical techniques
Arthroscopy is used to treat the following conditions:
- Unfixed bone pieces
- Ripped or damaged cartilage
- Joint lining inflammation
- Ligament tears
- Bruising within joints
Results of Arthroscopy
After the procedure, you should be able to start doing a mild activity and desk work again in a few days. Within one to three weeks, you should be able to drive once more, and a few weeks later, you should be able to perform more demanding activities.
But not everyone recovers in the same way. It may be necessary for you to undergo more extensive therapy and recuperation.
As soon as possible after the arthroscopy, your doctor will go over the results with you and might even send a written report. In follow-up appointments, your surgeon will continue to keep an eye on your development and deal with any issues.
For further information please access the following resources:
Emergency : +91 89686 77907
Front Desk : +91 98018 79584
Page last reviewed: Mar 6, 2023
Next review due: Mar 6, 2025







.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)