Legionnaires Disease Explained : Everything You Need to Know
755
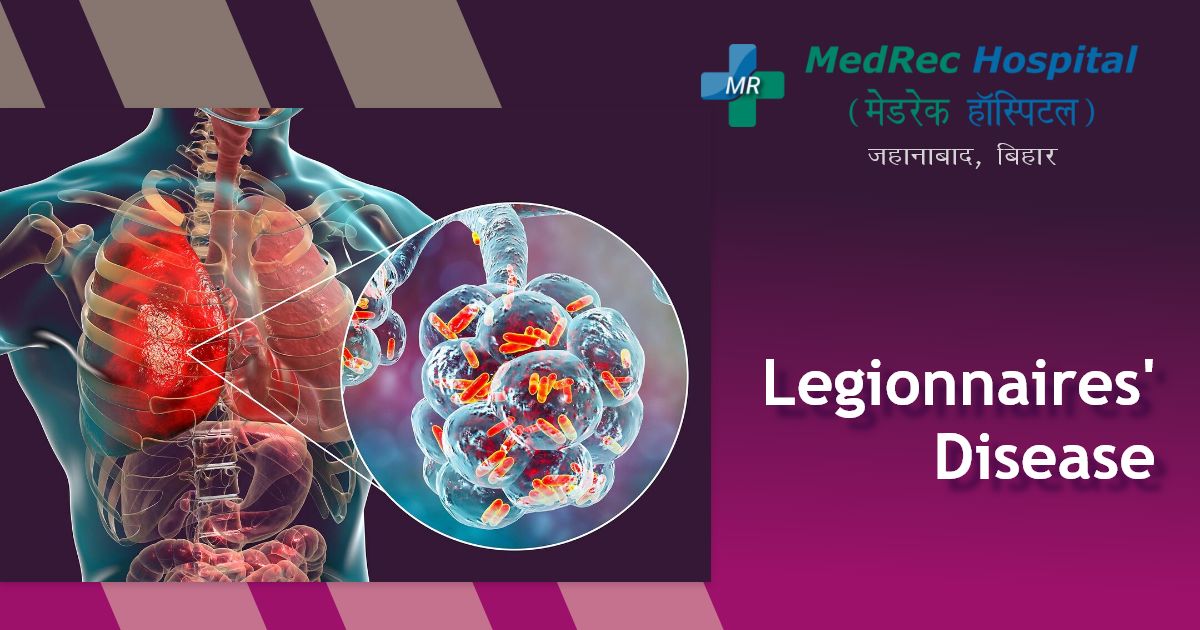
A severe form of pneumonia, or lung inflammation typically brought on by infection, is known as legionnaires' disease. It is brought on by the legionella bacteria.
The majority of cases of Legionnaires' disease are caused by breathing soil or water-borne germs. Legionnaires' disease is more likely to affect older people, smokers, and people with compromised immune systems.
Pontiac fever, a less severe condition similar to the flu, is also brought on by the legionella bacteria. Pontiac fever often goes away on its own, but Legionnaires' disease can be lethal if left untreated. Although Legionnaires' illness can typically be cured with rapid antibiotic therapy, some patients still experience complications.
If you breathe in tiny droplets of water that contain the infection-causing bacteria, you might acquire Legionnaires' disease.
Typically, it is contracted in establishments where the bacterium has entered the water supply, such as hotels, hospitals, or businesses. It is less likely that you will get it at home.
Things like air conditioning units, humidifiers, spa pools, and hot tubs can cause Legionnaires' disease. It can also be caused by faucets and showers that are rarely used
Normally, you can not obtain it from ingesting water from sources including ponds, lakes, and rivers that have infected individuals
Causes
Most instances of Legionnaires' illness are caused by the bacteria Legionella pneumophila. Legionella bacteria can be found in soil and water outside, although they seldom cause diseases. Yet, human-made water systems like air conditioners can support the growth of legionella bacteria.
The majority of outbreaks of Legionnaires' disease have happened in large buildings, possibly because complicated systems make it easier for the bacteria to thrive and spread. Legionnaires' disease can be contracted via household plumbing, though. Moreover, air conditioners in cars and homes do not need water to chill.
The majority of cases of legionella infection are caused by inhaling minute water droplets carrying the bacteria. This might be water from a huge building's ventilation system or the spray from a shower, faucet, or whirlpool. Emergencies have been connected to:
- Whirlpools and hot tubs
- Air conditioning system cooling towers
- Heaters and hot water tanks
- Artistic fountains
- Watering holes
- Childbirth pools
- Consuming water
The virus can also spread through other means besides inhaling water droplets, such as:
Aspiration. This happens when you drink unintentionally and cough or choke, which causes liquids to enter your lungs. You may get Legionnaires' disease if you aspirate water contaminated with legionella bacteria.
Soil. A few people have developed Legionnaires' disease after using contaminated potting soil or working in gardens.
How to check if you have Legionnaires Disease?
If you suspect you have come into contact with the legionella bacterium, consult a doctor. The recovery time can be shortened and significant consequences can be avoided by identifying and treating Legionnaires' illness as soon as feasible. Early therapy is crucial for those who are at high risks, such as smokers or elderly people.
Risk Factors
The legionella bacteria do not always cause illness in their victims. You have a higher chance of getting the illness if you:
Smoke. Smoking affects the lungs, increasing your risk of developing any kind of lung infection.
Possess a compromised immune system. HIV/AIDS, as well as several medicines, particularly corticosteroids and those used to prevent organ rejection following a transplant, may be to blame for this.
Have a major illness, such as chronic lung disease. Emphysema, diabetes, renal illness, and cancer are examples of this.
Certain Environments. At hospitals and nursing homes, where germs may spread quickly and residents are more prone to illness, legionnaires' disease can be a concern.
Symptoms
Typically, two to ten days after exposure to the legionella bacteria, the illness known as legionnaires' develops. Often, it starts with the following warning signs and symptoms:
- Muscle pains and headaches
- Perhaps 104 F (40 C) or greater fever
You will start to experience more symptoms by the second or third day, which might include:
- Coughing, which occasionally produces blood and mucous
- Breathing difficulty
- Chest pain
- Symptoms of the digestive system, including nausea, vomiting, and diarrhoea
- Dizziness or other mental modifications
Although the lungs are the main organs affected by Legionnaires' disease, the heart and other organs can also get infected on rare occasions.
Pontiac fever, a minor variant of Legionnaires' disease, can include fever, chills, headaches, and muscular pains. Your lungs are not infected with Pontiac fever. These symptoms frequently disappear in two to five days.
Prevention
Legionnaires' disease outbreaks may be stopped, but doing so demands that buildings have water management systems that make sure the water is checked and treated often.
Avoid smoking to minimise your own risk.
Treatments
Antibiotics are used to treat legionnaires' illnesses. The likelihood of experiencing significant problems decreases with the timing of therapy initiation. Treatment frequently necessitates hospitalisation. Pontiac fever does not require medical attention and resolves on its own.
If Legionnaires' disease is found to be present in your body, you might need to visit the hospital.
In-hospital care may consist of:
A gadget to help you breathe oxygen using a face mask or tubes in your nose and intravenous antibiotics.
You might be allowed to take antibiotic pills at home after your condition starts to improve. A course of antibiotics typically lasts one to three weeks.
Although most individuals recover completely, it may take a few weeks before they feel like themselves again.
Complications of Legionnaires Disease
Many potentially fatal consequences of the legionnaires' illness include:
Respiratory malfunction. This happens when the lungs are unable to expel enough carbon dioxide from the blood or provide the body with adequate oxygen.
Stomach shock. This occurs when blood supply to important organs, particularly the kidneys and brain, is reduced as a result of a significant, abrupt drop in blood pressure. The heart tries to make up for this by pumping more blood, but the added strain eventually makes the heart weaker and lowers blood flow even more.
Chronic renal failure. This is when your kidneys suddenly lose their capacity to remove waste from your blood. Dangerous amounts of fluid and waste build up in your body when your kidneys fail.
Legionnaires' illness can be lethal if it is not properly treated.
For further information please access the following resources:
Emergency : +91 89686 77907
Front Desk : +91 98018 79584
Page last reviewed: Mar 16, 2023
Next review due: Mar 16, 2025







.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)