Nail Fungal Infection : Know The Prevention And Treatment Options
681
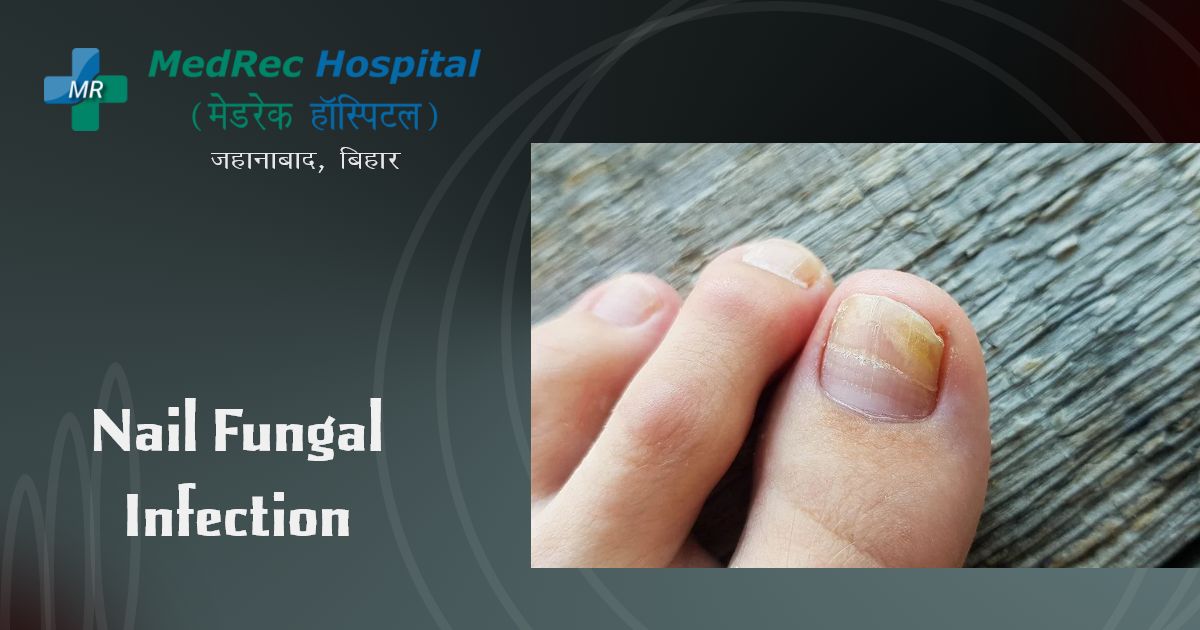
A frequent nail infection is nail fungus. It begins as a white or yellow-brown area under the tip of your fingernail or toenail. The nail may get discolored, thicken, and disintegrate at the edge as the fungal infection spreads deeper. Several nails may be impacted by nail fungus.
You might not require therapy if your illness is not troubling you and is moderate. Self-care measures and drugs may be helpful if your nail fungus is uncomfortable and has thickened your nails. Even with effective therapy, nail fungus frequently returns.
Onychomycosis is another name for nail fungus. An athlete's foot is a fungal infection that affects the flesh of your feet between your toes (tinea pedis).
Causes
Nail fungus can be caused by a number of fungi (fungi). The dermatophyte kind is the most prevalent. Mold, bacteria, and yeast can all result in nail infections. Green or black staining is typically the outcome of a bacterial illness.
A fungal infection of the nail can migrate to the foot, and a fungal infection of the foot can travel to the nail (athlete's foot). A gym shower's floor tile or the interior of a pair of black, sweaty, wet shoes are examples of places where you might come into contact with the fungus and become infected.
How to check if you have Nail Fungal Infection?
If self-care measures have not worked and the nail starts to get thicker, more discolored, or malformed, you might wish to consult a doctor. Also, discuss the following concerns with your healthcare professional:
- You believe you have nail fungus and diabetes.
- Surrounding the nails in blood
- Discomfort or swelling around the nails
- Having trouble walking
Risk Factors
The following things can make you more likely to get nail fungus:
- Greater age
- Wearing footwear that causes significant foot perspiration
- Having experienced athlete's foot in the past
- Wearing bare feet in moist public spaces like showers, gyms, and swimming pools
- Having a tiny wound on the skin or nails
- Having a skin ailment like psoriasis that damages the nails
- Having diabetes, blood flow difficulties, or a weakened immune system
Symptoms
One or more of the following nails are among the signs of nail fungus:
- Thickened
- Discoloured
- Broken, crumbly, or misshapen
- Not attached to the nail bed
- Although it can damage fingernails, stinky nail fungus is most frequently found in toenails.
Prevention
The following behaviors can aid in preventing athlete's foot, which can result in nail fungus, as well as nail fungus or reinfections:
- Keep your nails dry and spotless.
- Regularly wash your hands and feet.
- After contacting an infected nail, wash your hands. After thoroughly drying, dust on some antifungal foot powder and hydrate your nails. Applying a nail hardener could assist to strengthen cuticles and nails.
- Trim your nails regularly. Nail edges should be filed smooth, and thicker regions should be filed down. Cut nails straight across. After each usage, disinfect your nail clippers. Allowing your nails to grow long gives the fungus additional areas to spread.
- Change your socks frequently during the day or wear absorbent socks.
- Pick shoes with breathable fabrics.
- Throw away worn-out shoes or treat them with substances that are antifungal or disinfecting.
- In the locker rooms and around the pool, wear shoes.
- Pick a nail salon that gives each client a manicure using sterile instruments. Or sterilize the equipment you use for at-home pedicures.
- Give up fake nail polish.
- If you have an athlete's foot, use an antifungal treatment to treat it.
Treatments
There is not always a necessity for toenail fungus treatment. Occasionally, self-care and over-the-counter medicines can eliminate the illness. If your illness does not get better, consult your doctor. How you should be treated depends on the type of fungus causing your issue and how severe it is. Observing outcomes might take many months. Additionally, recurring infections are frequent even if your nail health becomes better.
Medications
Your doctor may prescribe antifungal drugs for oral usage or topically on the nail.
Oral antifungal medications. These medications are frequently chosen initially. Itraconazole is one alternative (Sporanox). With the aid of these medications, a new, clean nail gradually replaces the diseased one.
This kind of medication is normally used every day for 6 to 12 weeks. The treatment's success will not be apparent until the nail has fully recovered. An infection may be gone after four months or more. In persons over 65, treatment success rates with these medications seem to be lower.
Antifungal medications used orally have the potential to harm the liver and result in a rash. Or, they could conflict with other prescribed medications. To monitor your progress while taking these kinds of medications, you might need to have periodic blood tests. Patients with congestive heart failure, liver illness, or those on certain medicines may not be advised to use oral antifungal treatments.
Drug-infused nail paint. Your doctor could advise ciclopirox, an antifungal nail polish (Penlac). Your diseased nails are painted with it. After seven days, you use alcohol to clear off the piled-on layers before starting fresh treatments. This sort of nail polish might be needed daily for almost a year.
Cream for treating nails. Your doctor could suggest an antifungal cream like efinaconazole (Jublia) or tavaborole (Kerydin). You apply this product to your damaged nails after soaking. These creams could work better if you thin the nails first. This facilitates the medication's penetration of the fungus beneath the hard nail surface.
To thin your nails, apply a non-prescription lotion containing urea. Or, your doctor could use a file or another instrument to smooth off the nail's surface (debride).
Side effects from anti-fungal nail lotions are possible.
Surgery
Your doctor could advise temporarily removing the nail so that the infection under it can be treated with an antifungal medication.
The most efficient but least utilized method is to have the nail and its root surgically removed.
Complications of Nail Fungal Infection
A severe case of nail fungus may be unpleasant and harm your nails permanently. If your immune system is impaired as a result of medicine, diabetes, or other problems, it might also result in additional severe infections that extend beyond your feet.
For further information please access the following resources:
Emergency : +91 89686 77907
Front Desk : +91 98018 79584
Page last reviewed: Mar 20, 2023
Next review due: Mar 20, 2025







.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)