Abscess- What they are and how to medically treat them?
1038
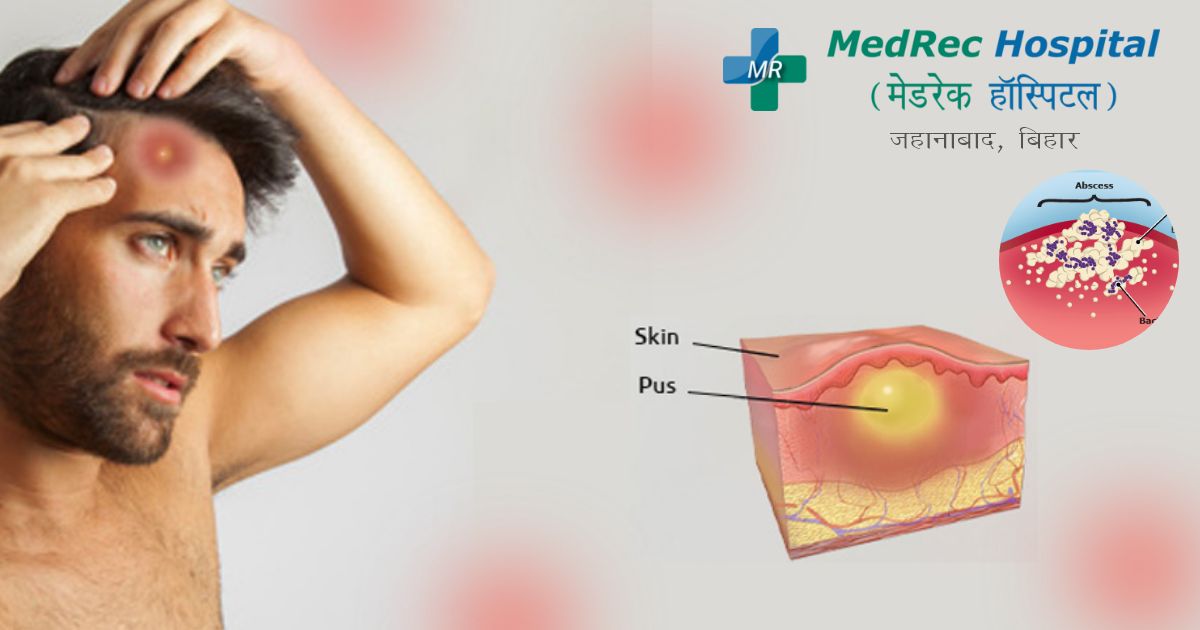
An abscess is a collection of pus-like lumps- that can build up anywhere around the body. There are different types of abscesses including Skin abscesses and Internal abscesses. Infections may cause these abscesses and a possible treatment option is a surgical treatment. Pus consists of white blood cells, bacteria, liquid and tissue that is dead. White blood cells can be living or dead.
An abscess can form anywhere on the body. The parts of the body where they are most likely to develop are the skin, around the mouth or on an organ.
Causes Of Abscess
Abscesses happen due to an infection with Staphylococcal bacteria. On the entrance of bacteria into the body, the body responds by sending white blood cells that respond to the infection. The immune system sends these white blood cells.
This causes the site to swell. Another name for this is inflammation. Nearby tissue dies. This creates a cavity that fills with a pus that leads to an abscess.
Pus contains dead tissue, white blood cells and bacteria. An abscess can get bigger, and become more painful as the infection spreads and more pus is made.
In special cases, the abscess can develop due to viruses or fungi.
How to check if you have an Abscess?
A skin abscess is a lump that is filled with pus. It is found on the outer layer of the skin. It can lead to a fever, infection and shivering. If the abscess is in the body signs to look out for are the following:
- Pain
- Very strong fever
- Feeling sick
Please contact your doctor if you have a lump on the skin or are displaying any of these signs.
To diagnose an abscess there are different tests that doctors can do.
The doctor will examine the area with a skin abscess. They make a testing sample and send this to the laboratory to determine which bacteria the pus has. This enables the doctor to choose the most effective treatment method.
If the patient has many skin abscesses, the doctor may ask for a urine sample to test for glucose. This helps with diagnosing diabetes if the patient has it. Patients that have diabetes can have lots of skin abscesses.
If the abscess is inside the body, a doctor can diagnose it by checking for signs and symptoms a patient may have. They can then refer you to a specialist for further tests.
Risk Factors Of Abscess
The following factors increase the chances of you developing an abscess:
- A patient with a weaker immune system
- Patients with diabetes
- Patients with inflammatory or infectious conditions
- Having a sample of the Staphylococcal bacteria
Most abscesses can develop in people that have very good health.
Symptoms Of Abscess
Symptoms can develop depending on the type of abscess and its location.
Skin abscess:
The following are signs of a skin abscess:
- Swelling under the skin or around the area
- Pain and the skin is tender
- The area is red and can be hot to touch
- Slow development of white pus under the skin area
- High fever
- Shivering
- The abscess can look like a boil
Internal Abscess:
The following are signs of an Internal Abscess:
- Pain and irritation in the area of the abscess
- High fever
- Lots of sweating
- Vomiting
- Nausea
- Shivering
- Stomach pain
- Severe weight loss and loss of appetite.
Prevention Of Abscess
Skin abscesses are caused by bacteria getting under the skin or around an internal site. Keeping skin clean and healthy can reduce the risk of a skin abscess developing.
The risk of bacteria spreading can be reduced by:
- Washing your hands
- Encouraging everyone at work or home to wash their hands often
- Not sharing baths and using different towels
- Waiting until skin abscesses are healed before using gyms or swimming pools.
- Not squeezing the pus area as this can lead to the spreading of bacteria and infection.
- Reducing the risk of skin abscesses by maintaining a healthy diet and managing weight
- With an internal abscess, as they are a result of other conditions, prevention can only occur if symptoms of the other conditions are managed.
Abscess Treatments
The main treatment options for abscesses are the following:
- A course of antibiotics
- Drainage of the site and abscess
- Surgery
Some abscesses may drain naturally and not require treatment. Warm compresses using a warm flannel can help with swelling and reduce the healing time.
Larger abscesses may require a course of antibiotics prescribed by your doctor. In larger and tougher abscesses, a procedure for drainage may be required. This prevents the abscess from growing and the infection from spreading.
Surgery will be performed to remove the drainage under anesthetic.
For Internal abscesses, pus is either drained using a needle or via surgery. A course of antibiotics is also prescribed to help stop infections and prevent spreading.
Complications of Abscess
There are many different types of abscesses and the more complicated ones are internal ones.
- Anorectal abscess- build of pus inside the bottom
- Bartholin’s cyst- a build-up of pus inside the Bartholin glands
- Brain abscess- Internal abscess with a life-threatening build-up of pus inside the brain
- Spinal cord abscess- Build of pus around a site on the spinal cord.
Internal abscesses can be life-threatening, more difficult to diagnose and more difficult to treat. Skin abscesses that are deeper in the skin can also be harder to detect in terms of symptoms.
Some symptoms link back to the part of the body that is infected. These include:
- Pain
- Fatigue
- High temperature
- Loss of appetite and weight loss.
For further information please access the following resources:
Emergency : +91 89686 77907
Front Desk : +91 98018 79584
Page last reviewed: Mar 2, 2023
Next review due: Mar 2, 2025







.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)